TYPE CLASSIFICATION ACCORDING TO OTM SEIFERT/DR. MED. STEINFELDT
The type classification presented internationally in 2001 supports us in orthosis consultation and subsequent care. In designing an orthosis, individual variations in design and construction are combined. The classification divides into 10 types of orthoses, depending on the impact of paralysis.
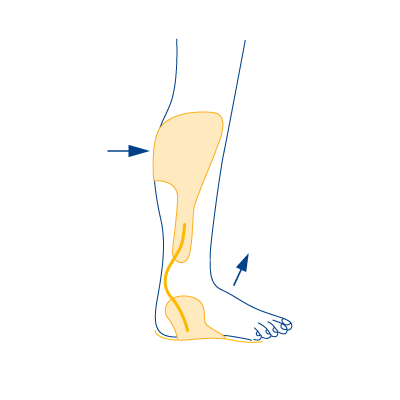
Type 1
- In case of failure of the foot-lifting muscles
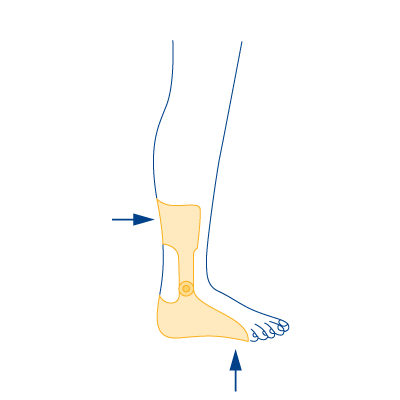
Type 2
- In case of failure of the foot-lifting muscles
- In case of ankle instability with misalignment (knock-knee or clubfoot)
- In case of leg length discrepancy
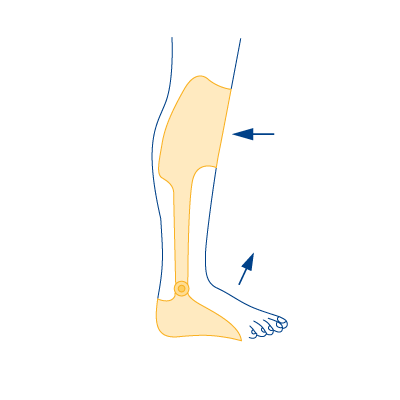
Type 3
- In case of weakness of the knee extensors
- In case of failure of the foot-lifting muscles
- In case of ankle instability with misalignment (knock-knee or clubfoot)
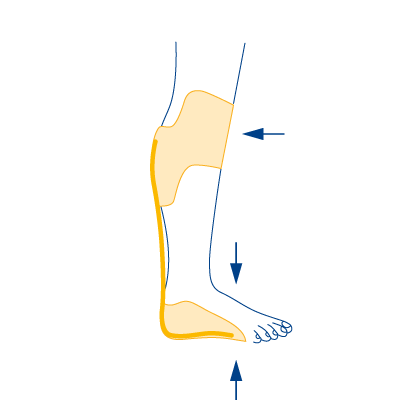
Type 4
- In case of the loss of the foot lifting and foot lowering muscles
- In case of mild hyperextension of the knee joint
- In case of ankle instability with misalignment (knock-knee or clubfoot)
- In case of leg length discrepancy
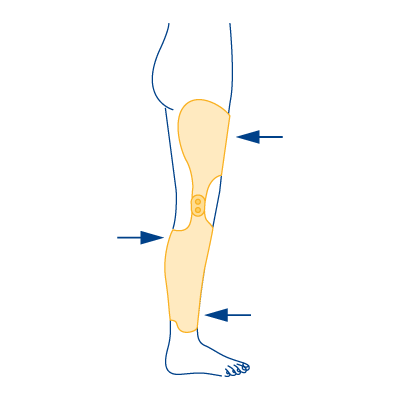
Type 5
- In case of severe hyperextension of the knee joint with weakness of the knee extensors
- In case of knee ligament instability (X- or O-legs)
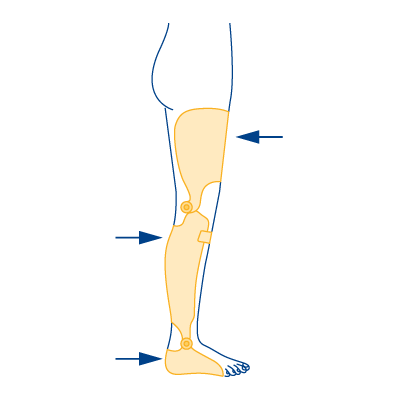
Type 6
- In case of weakness of the knee extensors
- In case of knee joint hyperextension
- In case of weakness or failure of the foot lifters, as well as in case of weakness of the foot droppers
Optional with carbon spring - For bilateral orthosis use
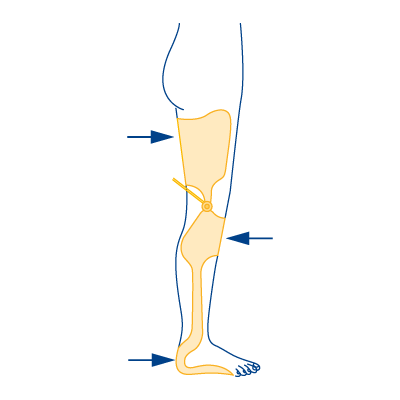
Type 7
- In case of knee extensor weakness
- In case of foot dorsiflexor weakness or failure
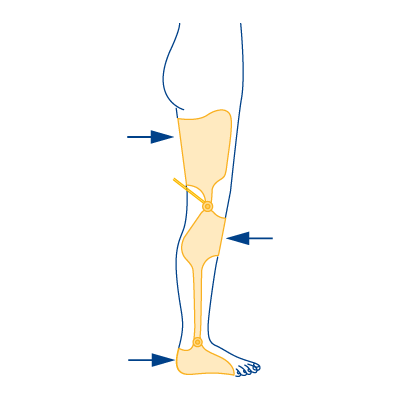
Type 8
- In case of knee extensor weakness
- In case of foot dorsiflexor failure
- In case of knee ligament instability (X- or O-legs)
- In case of ankle instability with misalignment (knock-knee or clubfoot)
- In case of leg length discrepancy
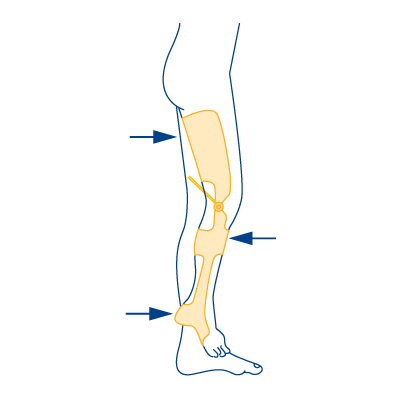
Type 9
- In case of knee extensor weakness
- In case of flexion contracture in the knee joint
- In case of equinus contracture with combined leg length discrepancy and clubfoot position
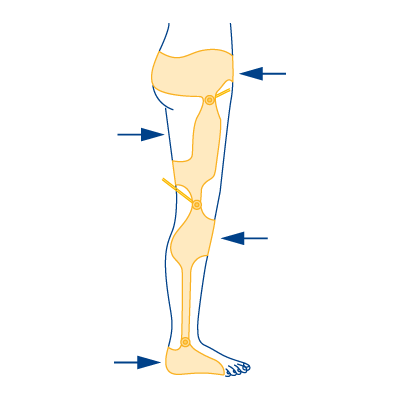
Type 10
- In case of loss of dorsiflexor muscles
- In case of ankle instability with misalignment (knock-knee or clubfoot)
- In case of knee extensor weakness
- In case of weakness or loss of hip extensor muscles
